Theoretical Framework : Mammalian Evolution
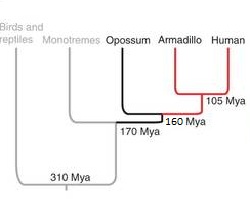
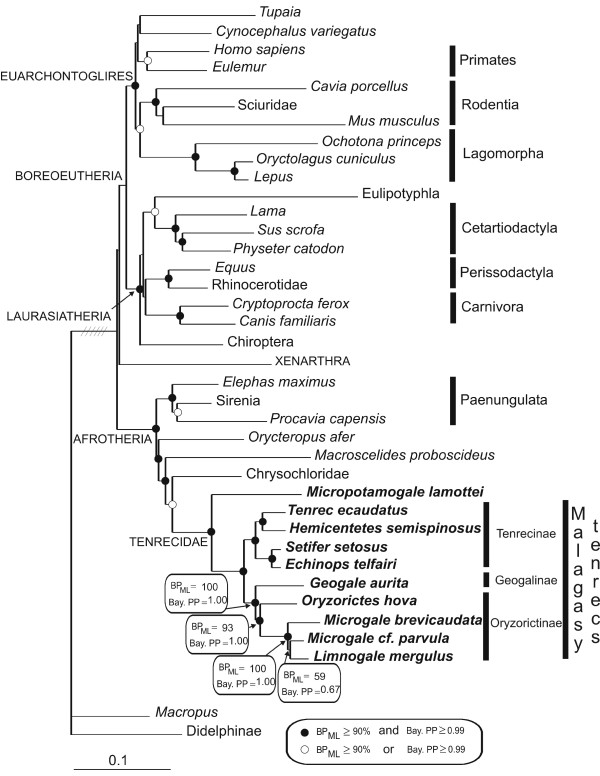
Mammals evolved from Therapsid ancestors. The Cynodonts gave rise to Northern Hemispheric Boreosphenidans and Southern Hemispheric Australopshenidans 190 Ma. The Australosphenidans gave birth to the Monotremes whereas the Boreosphenidans became Therians that split into Metatherians and Eutherians 165 Ma. The Eutherians created Xenarthrans and Afrotherians. Afrotherians + Xenarthrnas created the Boreotherians . Boreotherians evolved into Eurachontoglires and Laurasiatherians.
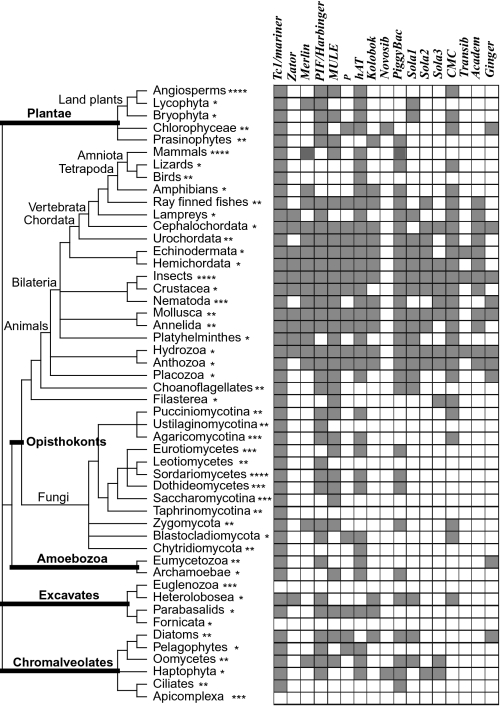
It is hypothesized that Transposons were responsible for the major species radiation events. They were initially delivered horizontally from Insects, Parasites, Plants, and other Animals via Viruses (Retroviruses and NCLDs). They subsequently expanded vertically after endogenization.
Ancient ‘genomic parasites’ spurred evolution of pregnancy in mammals
Rolling-circle transposons catalyze genomic innovation in a mammalian lineage.
A Hermes-Like hAT superfamily transposon integrated into the ancestor of mammals and provided the ZBED6 transcription factor
Eutherian mammals evolved from Metatherians 160 million Years ago (ref 1) by the acquisition and intrachromosomal spread of the MER20 Transposon.
Horizontal transfers of Mariner transposons between mammals and insects.
An example of the earliest eutherian mammal is Juramaia sinensi . Recent fossil discoveries suggest that it is the first mammal to start climbing trees and preceeded Eomaia by about 35 million years. Its existence correlates with molecular clock DNA studies showing the divergence of eutherian and metatherian lineages occuring 160 million years ago. It is hypothesized that tree climbing (conifers, gingkoes, and cycads ) and use of this new canopy ecosystem preceeded and influenced the development of placental birth. The shrew like lifestyle of these early eutherians included a diet of insects, worms, bark, and leaves. New viruses would have been ecologically exposed to these early eutherians and contributed to species radiation events / “punctuated equilibrium” episodes .
Xist RNA gene evolved in Eutherians from pseudogenization from a protein coding gene (RNA is involved in X chromosome inactivation )
Transposition of SRY to the Y chromosome in ProSimians 50-66 Mya
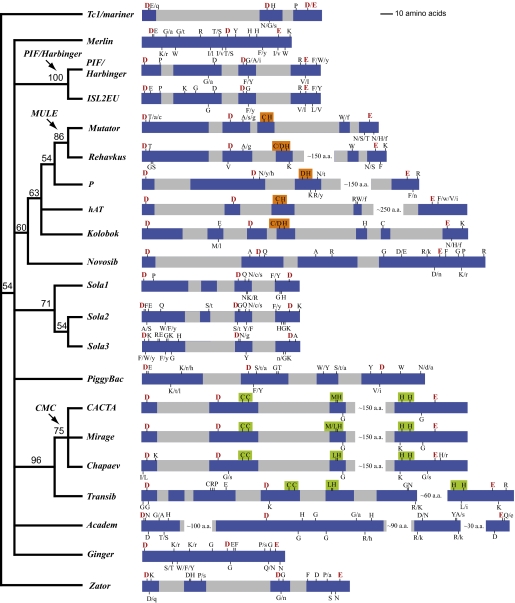
Mammalian DNA Cut and Paste Transposon Superfamilies:
Merlin/IS1016
Tcl/Mariner/IS1
Mule
hAT ( Ac group: Ac,hobo,hermes, herves, Tam3,Tol2 and Buster group: Buster and Spin ) ? Mx/rMX, Tag1, Bg, Tgf2 (may not be present in all mammals)
PiggyBac
Chronological Order of All Transposon Insertions into The Mammal Lineage leading to Humans:
DNA Cut and Paste Transposon Superfamilies
Other DNA Transposons
Helitrons —Rolling Circle Like Method of Copying and then Pasting .. Found in Brown Bat.. Myotis lucifigus and in Polydnaviruses of Wasps.
Mavericks/Polintons– protein primed DNA polymerase dependent copying and then Pasting. ( Not found in Mammals or Plants) present in virophages
.gif)