Neonatal Surfactant – Supports alveolar development and has antiviral properties through pathogen recognition receptor proteins similar to mannose/ galactose binding lectins.
Dextran Sulfate like Mucus – Bind extracellular viruses and promote their clearance
Decreased ACE-2 Receptors – Reduce viral entry into the cell
IFITMs – Inhibits viral fusion as the plasma membrane but might stimulate viral endocytosis. IFITM3 has a particularly important role with COVID -19 restriction. It is induced by class I interferons along with IFITM2, CLEC4D, LY6E, and UBD. IFITM3 interacts with or is counteracted by viral proteins M and Orf9b.
cGAS-STING System– Covid -19 has major effects in both inhibiting and delaying the over- stimulation of this system. Its interactions offer strategies for treating severe Covid -19 as well as promoting mild or asymptomatic Covid -19 infection.
Complement Cascade System: Factor C5a and the C5aReceptor on Cells are elevated in severe COVID-19 infection. Over activation of this system contributes to neutrophil infiltration , NETOSIS and the over activation of the cGAS-STING pathway. Binding C5a with antibodies or preventing it from activating its receptor are potential strategies for COVID -19 infection treatment when viral load surpasses a certain threshold that removes sufficient factor H from its surface binding at heparan sulfate sites. Reduced Factor H as the surface of cells allows the membrane attack complex to form via the Alternative Complement Pathway and attack healthy cells rather than the virus itself. Inhibitors of Factor D can prevent this from happening.
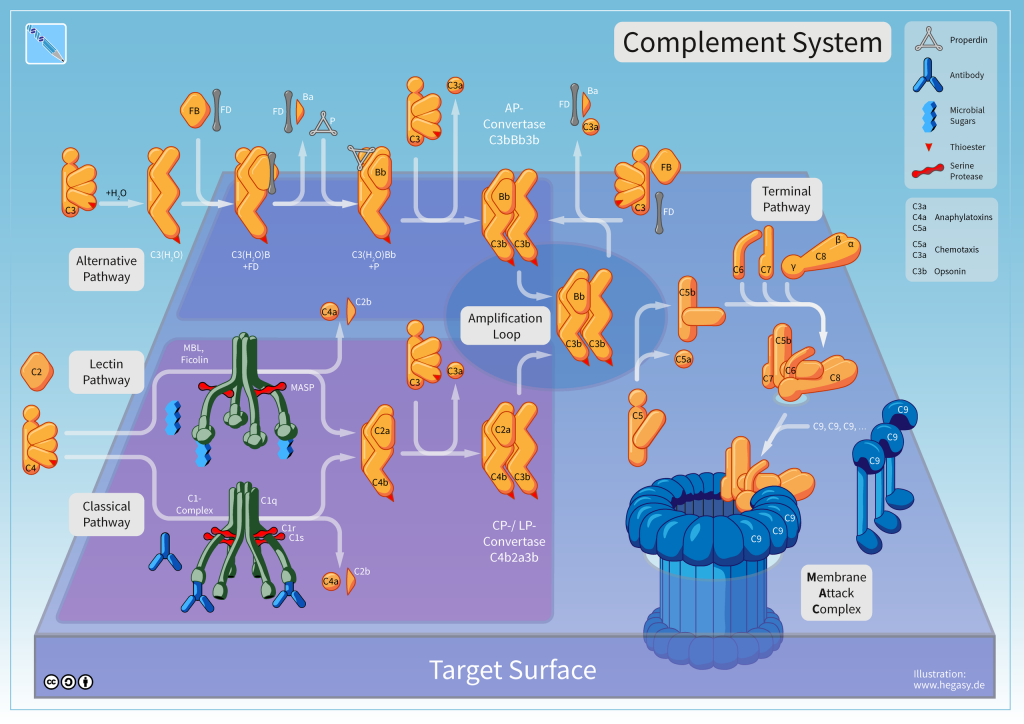
Mannose Binding Lectin – An Acute phase reactant blood protein. plays a role in both the initial clearance and pathology of COVID-19 infection via the Lectin Pathway of Complement Activation. It is elevated in cases of severe COVID-19 with coagulopathy problems. Ethnic variations in its basal level may contribute to some genetic related reasons for ethnic disparity in COVID 19 incidence or severity. Other Collectins and Ficolin’s may also play a role in first line of immunity protection or later problems with complement cascade dysfunction.
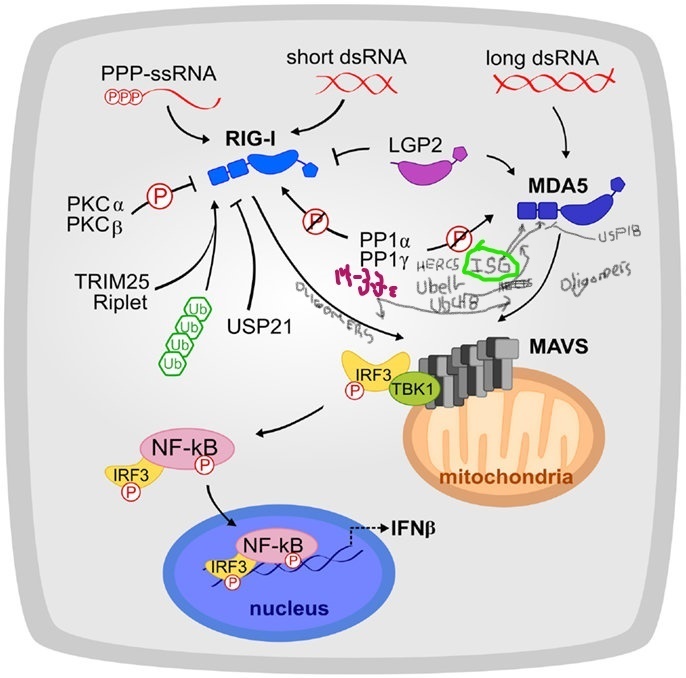
RIG-I/TRIM25 + Lnczc3h7a RNA + MDA5 + MAV and DDX60 System
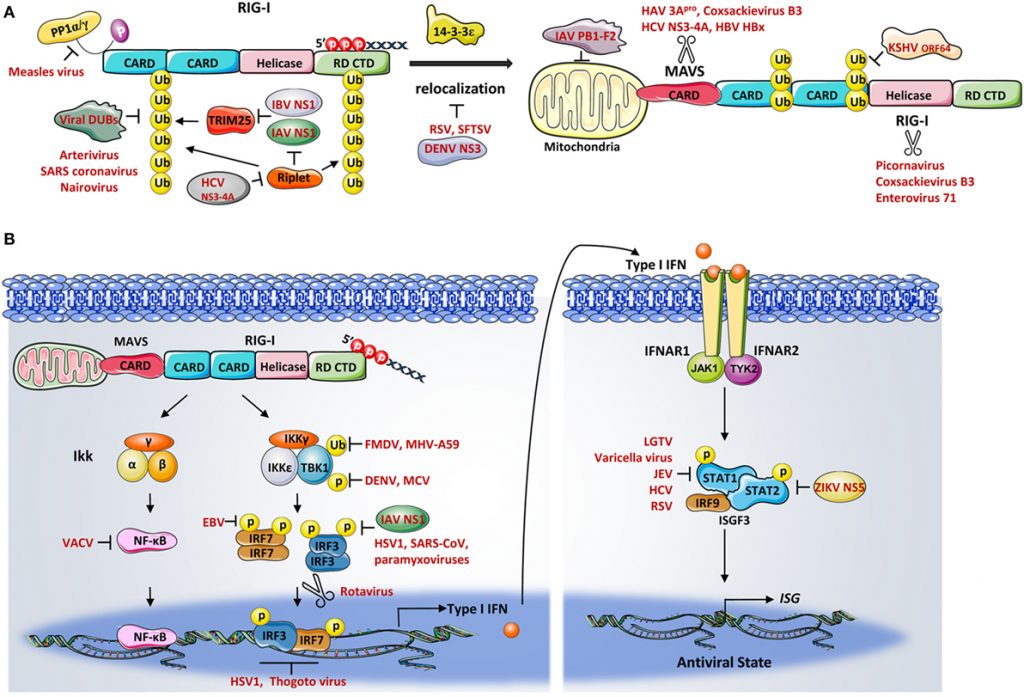
Rig-I is activated by recognition of foreign mostly short dsRNA while MDA5 recognizes a complementary group of long pathogenic dsRNA (including coronavirus RNA). The COVID-19 virus has evolved anti-Rig-I and MDA5 mechanisms that prevent it from meeting its role in innate immune defense. The impediments that the virus promotes through NS1 and other viral proteins could be targets for treatment to enhance clearance and abortion of viral infection.
TLR7/Toll Receptor 7 – Major endosomal pattern recognition protein active at the Endosomal Entry stage of Viral infection. Recognizes viral ssRNA. Defects in the X chromosome gene for TLR7 are associated with severe COVID-19 infection.
LncRNA-ZC3H7A Protection System – Part of MAV/RIG-1 defense system.
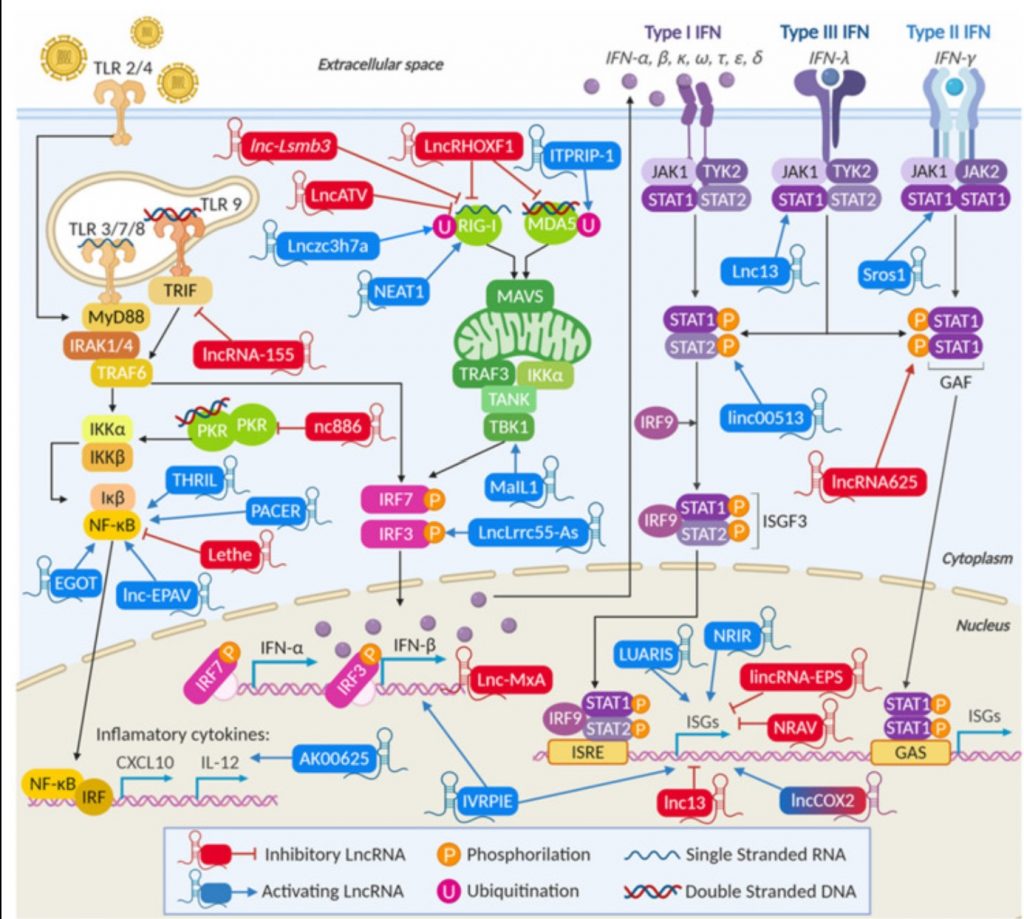
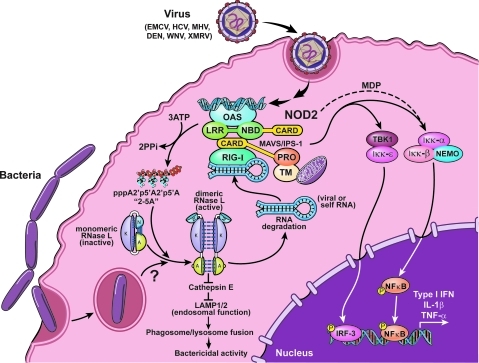
RNAse L and RNA Stress Granule Formation
Ubiquitin -Proteosome System is also regulated by ISGlyation (ISG15, USP18 ) and Sumoyalation
ZAP (Zinc Finger Antiviral Protein) – Restricts COVID-19 particularly the long isoform. It binds CpG dinucleotides and promotes the degradation of RNA.
Mitochondrial DNA – Is used in NETOSIS and Mitochondrial DNA Traps. May play more of a pathological role in Severe Covid disease.
Peroxisomes – Help degrade viral lipids and clear virus particles . Some viral proteins and known to interact with peroxisome specific proteins such as …..
Hypermutation agents – ie APOBECG3 are not as active as restriction factors as they are in retroviral infections but may still play an unknown role in host restriction.
Interferon Stimulated Gene Products with anti-coronaviral /restrictive activity.
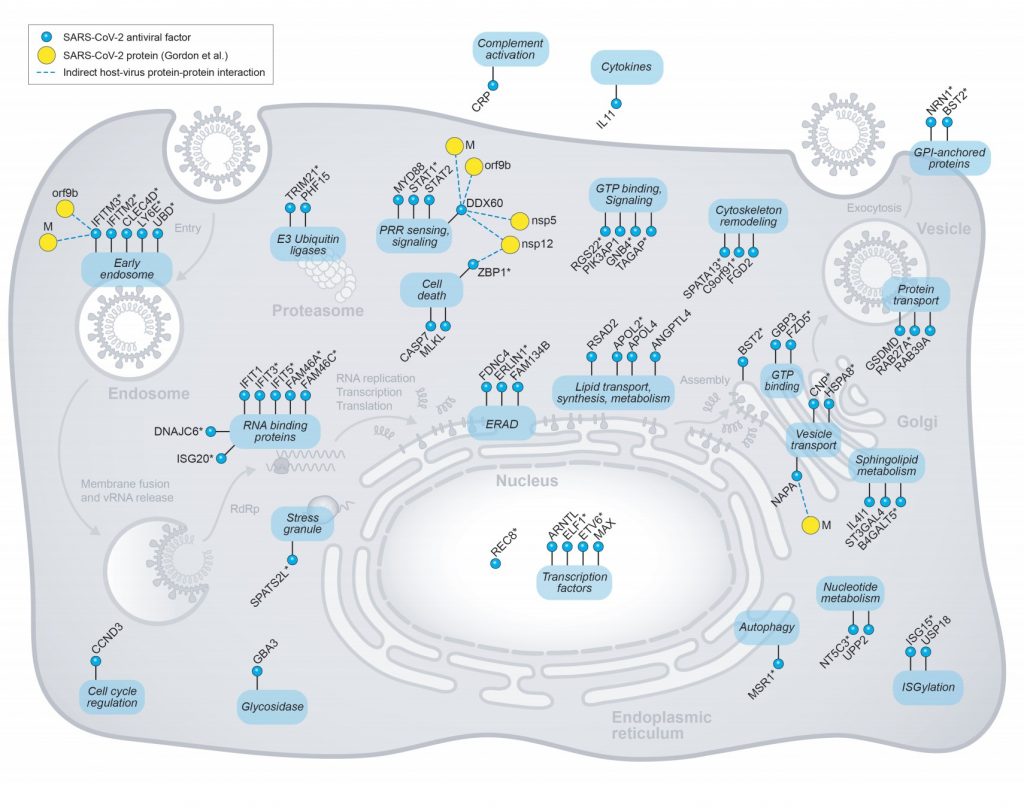
ER Associated Degradation

Viral RNA binding Host Restriction Factors :
MicroRNAs may be associated with Age and Disease Related risks for Severe COVID Infection. Citations to article