It is estimated that protoplanet Earth had a differntiated
core,mantel, and crust within 30 million years of
Proplyd formation. Matter on ProtoEarth would have been exposed to infrared
radiation from the Protosun as well as high energy gamma,
cosmic, UV, and xrays from Extrasolar system Sources. The infrared
radiation would have provided some stable zones of hydrocarbon and water
phase transitions.
Numerous supernovas would have occured in our nearby Star Cluster
and therefore modern cellular based life forms would have had a
difficult physiochemical environment for existence. However, other
forms
of life utilized these high energy opportunities to convert energy
into the work required for organization of carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, sulfur,
and metal ion molecules into ProtoCells. The amount of energy required for
this conversion can be theoretically estimated using Information Theory.
The estimation can then be used to provide timeline for the
energy to entropy conversion steps during ProtoCell Development. The exact
nature of those steps can be further elucidated.
Theia and ProtoEarth Collided 4.5 Billion Years Ago.
ref 1, 2 .Earth
had an iron core at the time of collision but the core of Theia
is not yet known. However, Theia is believed
to have
formed further away from the Sun and therefore would have contained
more volatile gases such as water, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen.
Evidence for the Great Impact Hypothesis comes from simulations,
earth & moon gravity maps, and zinc isotope analysis.

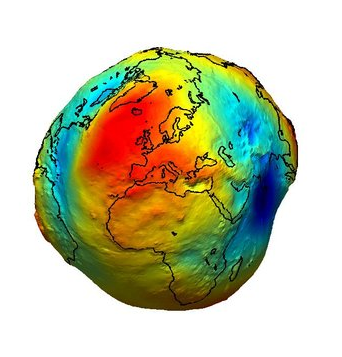
Current Gravity Map of Earth. Can you see the scars of impacts ?
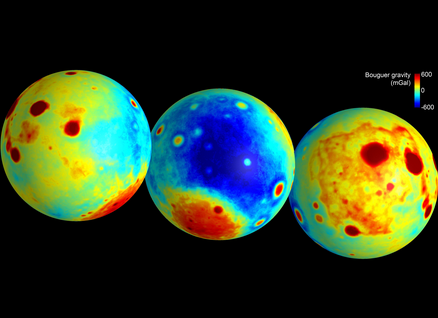
Gravity Maps of the moon. Scars from prior impacts more readily
visible.

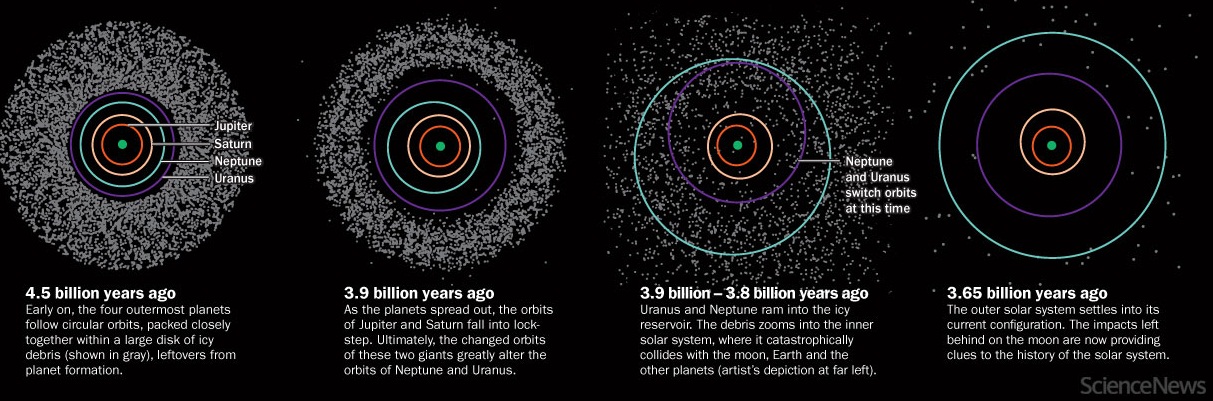
Late
Heavy Bombardment 3.85 -3.95 Billion years ago with temperatue spike
on Earth.
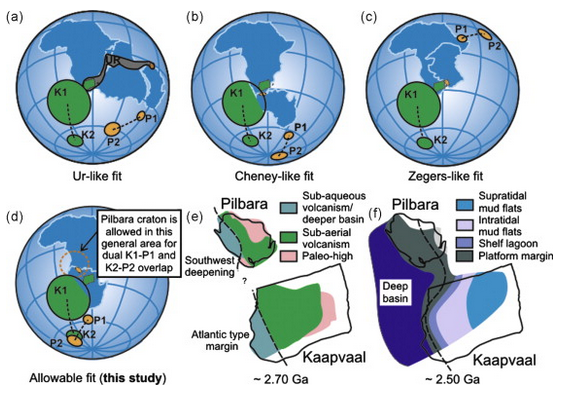
Vaalbara Supercontinent
is believed to have formed 2.7 Ba along with or including a possible UR
continent. Evidence exists for a biogenic land based sulfur oxidation process
existing
at that
time.
This suggest the presence of some minimal oxygen possibly from symbiotic
cyanobacteria.
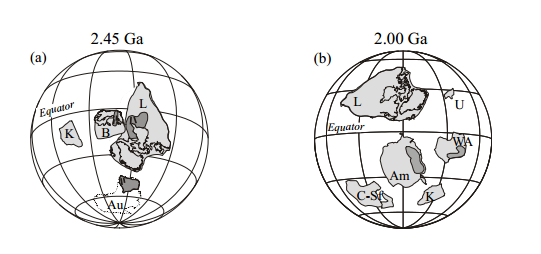
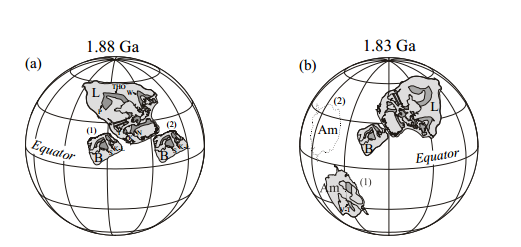
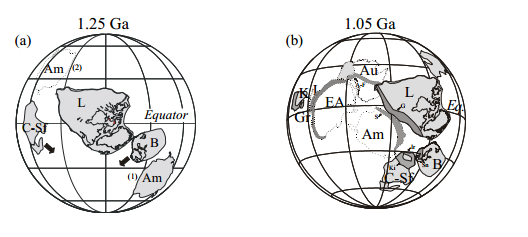
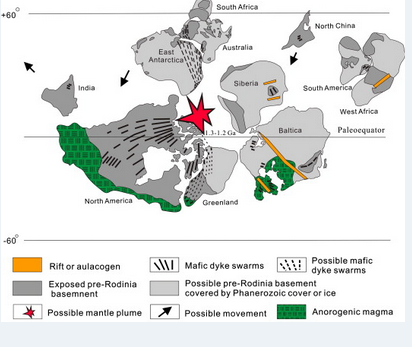
Breakup of Columbia/Nuna Supercontinent 1.30 -1.20 Ba
Models of Temperature, CO2, and Sea Level History
Ref 1.
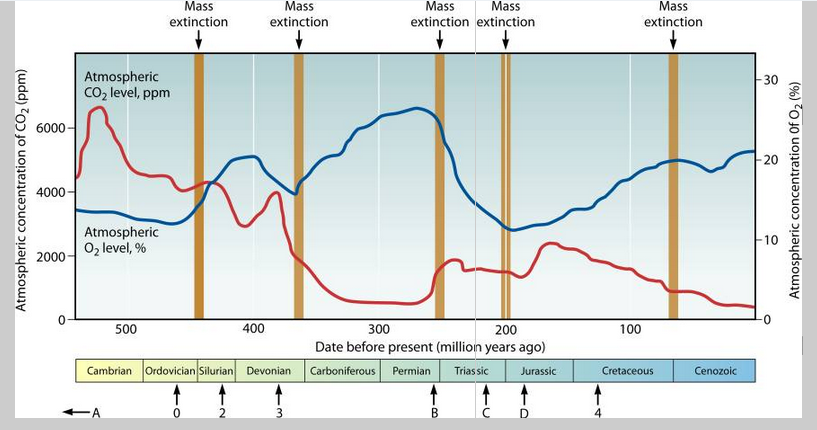
Atmospheric Oxygen Levels
Eukaryot Cell. 2011 July; 10(7): 856–868.
doi: 10.1128/EC.00326-10
Do Red and Green Make Brown?: Perspectives on Plastid Acquisitions within
Chromalveolates Richard G. Dorrell* and Alison G. Smith
Atmospheric Ozone Levels
Atmospheric Hydrogen, Helium, Argon, and Nitrogen Levels
Nickle starvation in oceans at 2.7B years ago. Nickle release
during Permian Extinction from Siberian Flats with increased Methanobacteria
activity.
Geophysical Sulfur Cycles mobilizing molybdenum, zinc, cobalt,
and iron,
Neobium concentrations in Crust
Sodium, Postassium, Phosphate, Chloride, Iodide, Fluoride,
Calcium, Magnesium, Manganese, Boron, Chromium, Ammonia,Hydrocarbon
Mineral Concetrations in Core, Mantle, and Crust
Nitrate Levels in Ice Cores
Carbon Isotope Levels
Hydrogen Isotope Levels : High level of protons during 3.4
Gya with decrease in H/D ratio over time. ( Proposed Loss of H to Space via
methanogenesis)
Oxygen Isotope Levels
Argon Isotope Levels
Uranium Concentrations in the Crust
Gold Crust Concentrstions
Silver Crust Concentrations
Earths potential history of exposure to supernovas and cosmic
rays.
Comparisons to Mars
No
methane, but evidence for a far thicker Martian atmosphere
Isotope ratios suggest that lots of Mars' atmosphere escaped into space
nifH archea.
Bibliography
Climate regulation and atmosphere evolution
The Hadean-Archaean Environment
Stanford Report, November 11, 2009
Stanford study: Earth's early ocean cooled more than a billion years earlier
than thought
Large Scale Ocean Circulation from Grace
New Spin on the Origin of the Earth and Moon
Gravitational Anomoly in Sri Lanka
Concentrically zoned pattern in the Bouguer gravity anomaly
map of northeastern North America
Development
of the negative gravity anomaly of the 85°E
Ridge, northeastern Indian Ocean – A process oriented modelling approach
The Indian ocean gravity low: Evidence for an isostatically
uncompensated depression in the upper mantle
Asteroidal impacts and the origin of terrestrial and lunar
volatiles
Icarus, Volume 222, Issue 1, January 2013, Pages 44-52
Francis Albarede, Chris Ballhaus, Janne Blichert-Toft, Cin-Ty Lee, Bernard
Marty, Frédéric Moynier, Qing-Zhu Yin